Customer Key in Subscription Commerce
Over the past few years, more businesses have been experimenting with subscription commerce. With companies becoming more innovative and competition heating up in different industries, businesses have to find ways to provide value to a sizeable market that is ready to pay for their services. Most cloud based companies are opting for subscription business models rather than other forms.
Why is subscription business model becoming the standard for most cloud based services?
Before starting a business, you have to understand your business model. This refers to how you are going to monetize your relationship with your customers. You can adopt a single or combination of monetization strategies which may include ad revenues, affiliate marketing, paid subscription, recurring subscription and so on. The type of monetization you opt for will mainly depend on your product and target market. For cloud based services, subscription is the best way of generating revenues.
Subscription Economy is the Future
Online commerce is moving towards subscription. Customers find it more convenient to subscribe for a service when they need it. With a subscription model, customers can choose the level of service they want and the frequency that they want to be billed.
Customers have different needs and what a small company may need in an invoicing software may be different from the needs of a large corporation. Subscription companies should therefore tailor their products to address the different needs of their markets. Customization can be done by having different levels of services, allowing for upgrades and so on.
For businesses, subscription services allow them to monetize their relationships with customers over time instead of fighting for one-time sales. A typical subscription company may start its users with a free trial and later upgrade its services to a paid one. Based on customers’ needs, the company can add upgrades or add-ons to continue generating revenue. With the future economy, it’s not about selling to the customer,but monetizing an ongoing relationship.
The Rules of Subscription Commerce
Some traditional commerce rules still apply to subscription services. However, there are other metrics that are particular to the subscription economy that a company should watch. These metrics include:
a) Number of customers. How many customers does you business have? Your customer base can determine your gross margins.
b) Average selling price. How much monthly recurring revenue is your business generating?
c) Close rate. How many customers convert from free trials to paid accounts?
d) Renewal rate. How much and how long can you keep your customers around? How many pay you again after the initial subscription period?
d) Gross margins. What is your total contract value and how long can you monetize a customer?
Existing relationships are driving customers today. Some of the leaders of subscription business are valued more than those in the traditional shipping business. Great examples of subscription services businesses include Salesforce.com and NetSuite.
Why Subscription Services?
With a traditional business, you make a sale and lose that customer after the transaction. After the sale, you wait to generate your next sale for a new customer.
On the other hand, with subscription services, you make a sale from your new customers and continue getting recurring revenue from them over time even as you get new customers. The recurring revenue comes from upgrades, add-ons, premium packages, etc.
Once you have a significant number of existing customers, you can focus more on providing value to them and be assured of recurrent revenue. If you are not in subscription business, you will have to focus your efforts on acquiring new customers, which is usually expensive than maintaining existing customers.
Strategies for Monetizing Your Customers
You can monetize your existing customers in different ways. Your monetization strategy may be determined by the stage of your business and your overall goals. Below are some monetization strategies:
a) Free Service or Tools
Most companies cast a wide net in the market with a free service. When customers sign up, the company can pursue them to consume more. As customers get going with the free service, the business can present more paid features to them. For example, Roost offers free social media tools to real estate professionals and then presents them with premium features. You can also take a look at Hubspot’s MarketingGrader. They offer a free tool to analyze your website and give valuable feedback on how to optimize your website better. Chargebee does this as well by providing a free forever sandbox for businesses and developers.
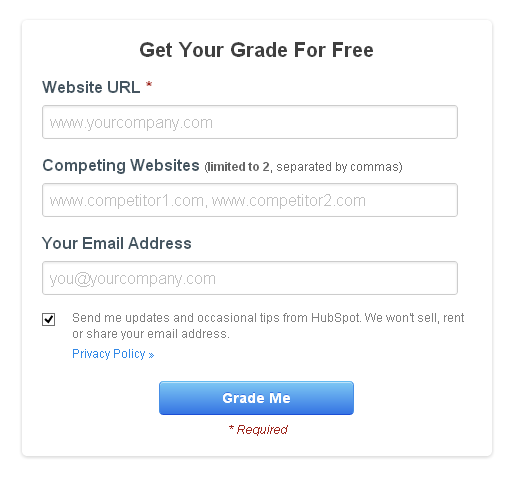
Hubspot Marketing Grader
b) Entry Paid Service with Free Trials
With this strategy, you put a very low entry point for your customers to try your basic services. You can then leverage your existing relationship and push for upgrades or higher paid packages that have more robust features and provider better value to customers. Unlike the free service model, you generate revenues from the start with low entry paid service. Ning is a good example that is following this monetizing model.
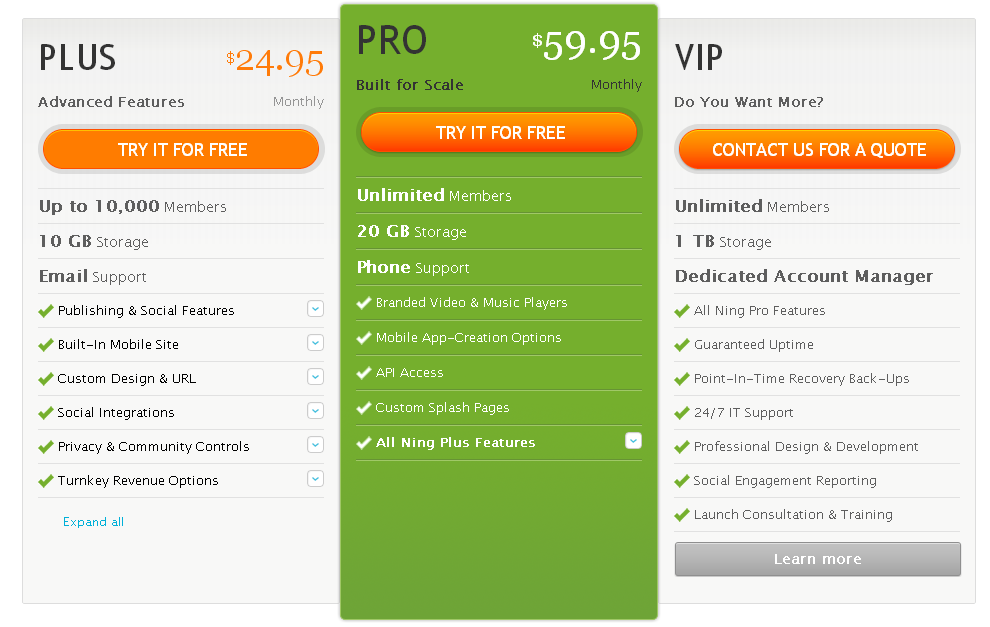
Paid Entry Service – Ning
c) Expansion
This strategy is mainly used by B2B companies. In an expansion model, you target an individual with your offer, develop a relationship with them and hope they will see the value of your product and sign up for a larger account. The larger account has limited users and may be ideal for a department and if a company wants your solution for all its departments, it can upgrade to an enterprise package. One company that is using the expansion model in Time Trade. The idea is leveraging an existing relationship with your one customer and hope an entire team will sign up.
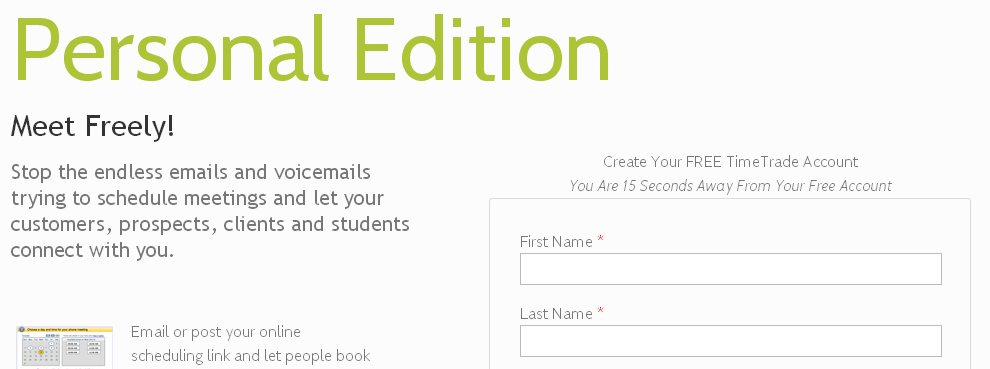
TimeTrade – Expansion Strategy
d) Upgrades and Add-ons
Upgrade is a common model with subscription services companies (similar to the entry paid service). Here, you simply have packages with different features that will suit your customer demographics. Customers can sign up for the package they want based on their needs or budget. Most web hosting companies use the upgrade model, whereby customers can sign up for Bronze, Silver or Platinum hosting, all of which come with different pricing and features. BigPond is one example in this category.
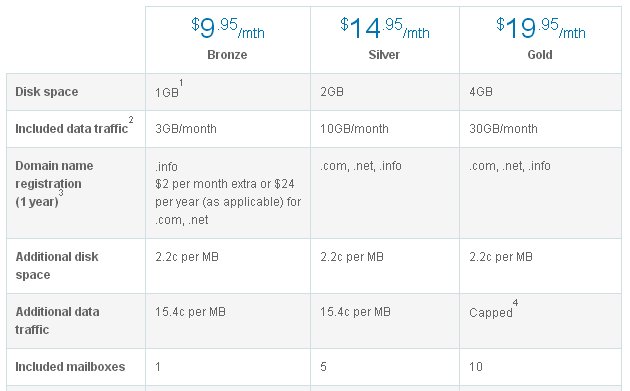
Upgrade Strategy – BigPond
Sometimes, business go through difficult times and may need to cut their spending. Therefore, it is important for subscription business to enable customers to down grade and you need to make sure that your billing system supports downgrade functionality.
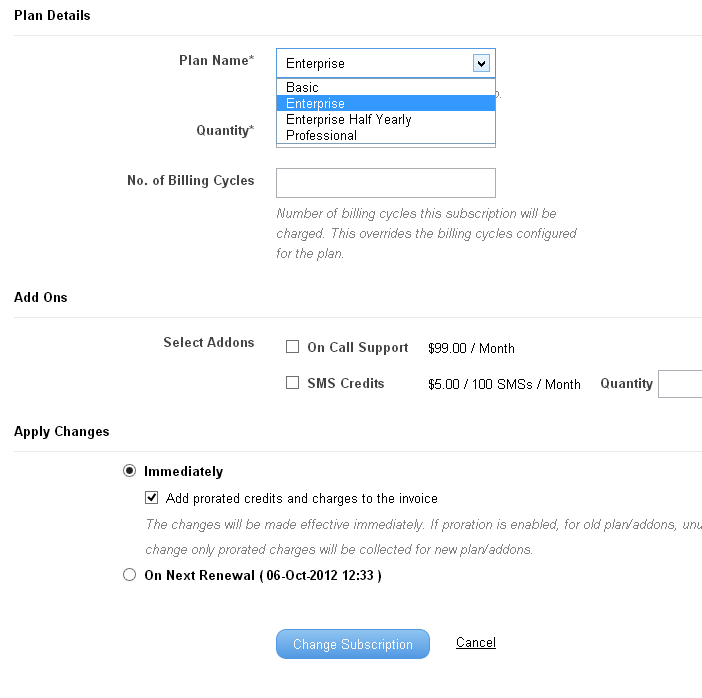
Downgrade Option in Billing System – Change Subscription as necessary
Challenges of Subscription Commerce
Subscription commerce has different challenges from what traditional businesses face. There are two main challenges of subscription commerce: growing the monthly recurring revenue (MRR) and reducing the churn rate.
Monthly Recurring Revenue: This is the amount of revenues that your business gets every month. The metric is determined by your service price and the number of customers that you have. To ensure your MRR grows, take care of your existing customers to ensure they do not downgrade or cancel their subscriptions.
Churn Rate: This is the percentage of customers that fail to renew their subscription every month. You should reduce the churn rate to as low as possible to improve your margins. Offering support to your customers is crucial to reducing the churn rate.
Apart from the above challenges, you also need to come up with pricing, bill and track payments, address subscription complexities, product upgrades, invoicing, measure metrics like total customer value and so on. Keeping tabs with all these metrics can be challenging, expensive and time consuming if you do not have the right tools in place.